
The significance of modern Core Banking Systems (CBS) cannot be overstated. Financial Institutions (FI) are substantially investing in upgrading their historical CBS in order to make banking services more accessible, flexible, customizable, and scalable.
Nevertheless, how can FIs ensure that the modern Core Banking System is utilized to its full potential?
The FIs should assure that their teams who use core systems, viz., customer interaction and support, finance, and product development, comprehend the key concepts of CBS and its modules.
Modules in Core Banking System
CBS is built on a network of integrated modules, each of which serves a distinct role during financial transactions. These modules work together to ensure that banking operations run smoothly, delivering efficiency, accuracy, and security.
Here are the 7 modules that aid the FIs processes and facilitate day-to-day banking operations.
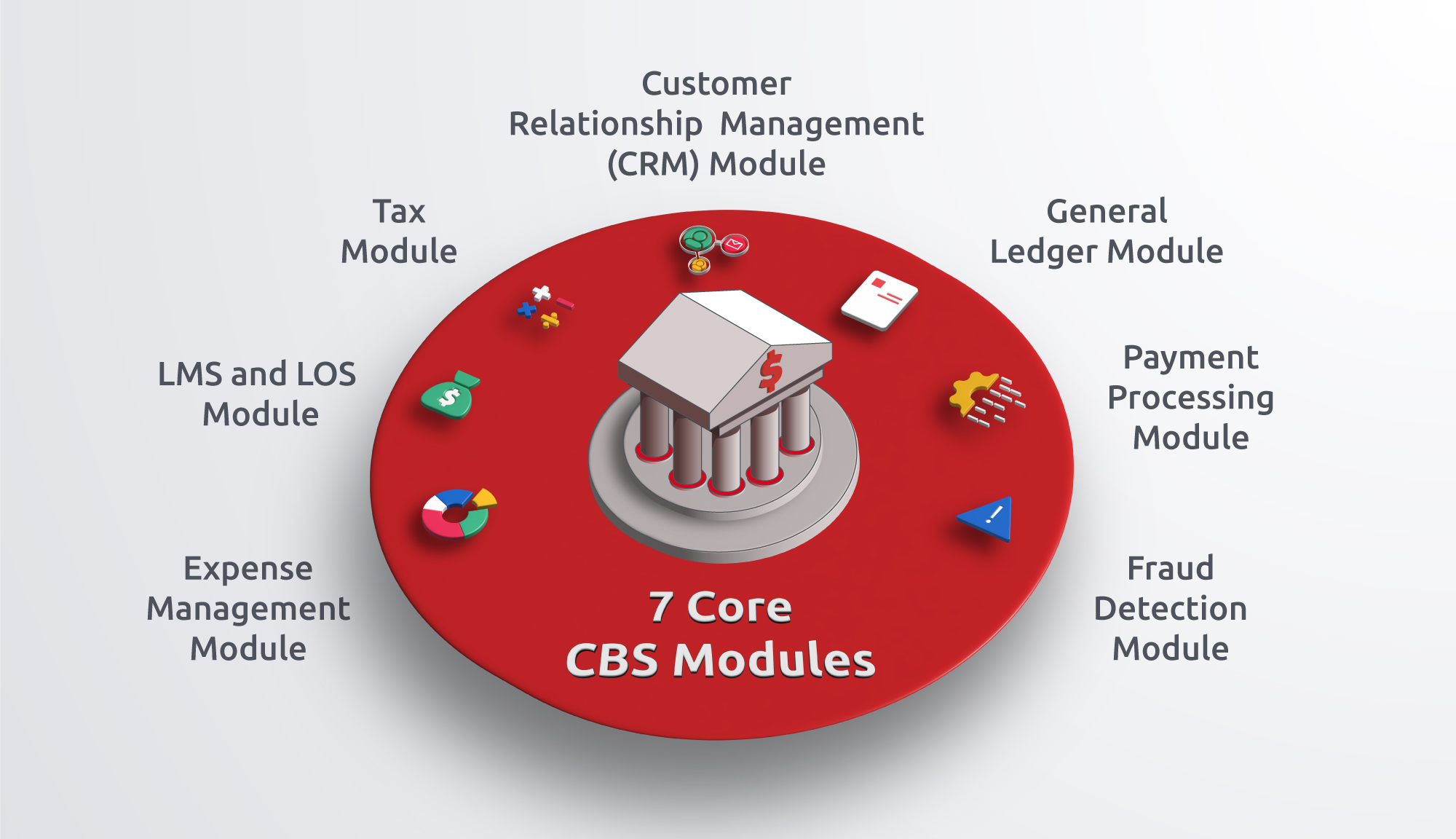
1. Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Module
Whenever a user opens a banking app, the CRM module greets them by name and provides personalized recommendations. The process exemplifies the essence of effective customer relationship management. Beyond just storing data, the CRM module enriches and customizes user interactions. During user logins, the CBS triggers its CRM module to present tailored experiences, such as targeted product offers, and to streamline interactions.
2. Payment Processing Module
The Payment Processing module in a CBS ensures precise and efficient transaction management. It handles various payments, including local and internal transactions, manages unknown payments, and interfaces with back-office forms, correspondent accounts, and currency exchange modules. It verifies transactions, calculates fees, and records all financial movements that encompass deposits, withdrawals, fund transfers, and bill payments. This crucial component guarantees streamlined FI operations.
3. General Ledger Module
The General Ledger (GL) Module operates as a centralized repository within the enterprise system, systematically recording all financial transactions. Its primary function is to maintain all accounting entities in balance and turnover. The module consolidates these balances across several logical levels, facilitating comprehensive informational and analytical reporting for effective financial management within the corporate world.
4. LMS and LOS Module
Loan Management System (LMS) automates and streamlines the whole loan process, from application to repayment, including customer information, propositions, and collections. It aids FIs in maintaining regulatory compliance by providing a centralized platform for creating, delivering, and tracking compliance training modules, ensuring all employees receive the necessary training, and generating detailed reports for auditing.
Loan Origination System (LOS), on the other hand, processes and appraises loan applications. Employing workflow technology, LOS controls, and monitors loan processing to reduce delays and inefficiencies associated with paper documents. It covers the entire loan origination process, from application submission to fund disbursal or application decline.
Both LMS and LOS optimize the loan lifecycle, automate lending processes, and provide tailored features that seamlessly integrate with existing systems, resulting in lower costs, higher efficiency, and increased customer satisfaction.
5. Fraud Detection Module
Fraud Detection Module benefits FIs by preventing illegal or destructive activities before they occur. Utilizing data analytics, machine learning, and behavioral analysis, fraud detection systems identify patterns of suspicious behavior to proactively safeguard against potential fraud. By integrating advanced real-time alerts, biometric authentication, and zero-trust principles, FIs can efficiently detect and mitigate fraudulent activities, thus bolstering stakeholder trust and compliance.
6. Expense Management Module
The Expense Management Module aids customers in methodically overseeing and controlling expenses, ensuring that budgets are not just created but strictly adhered to. Through systematic monitoring, the module ensures optimal utilization of financial resources for smarter financial decisions. It further optimizes reimbursement processes, reduces errors, and contributes to overall improvement.
7. Tax Module
The Tax Module maintains financial integrity and manages taxes with automated precision, from income to corporate. This eases tax-related responsibilities for FIs and their customers. Integrating the tax module enhances efficiency in handling tax obligations, contributing to smarter, simpler, and more secure modern banking practices.
All the core banking modules discussed above operate seamlessly behind the scenes to ensure a smooth and secure banking experience. As FIs invest in upgrading their legacy systems, the integration of these modules not only streamlines transactions but also enhances customer experiences, fortifies security measures, and drives operational excellence.
Want to know more about Core Banking Systems?
Write to us at business@m2pfintech.com. We’ll reach out to you as soon as possible.
Subscribe to our newsletter and get the latest fintech news, views, and insights, directly to your inbox.
Follow us on LinkedIn and Twitter for insightful fintech bytes curated for curious minds like you.



0 Comments