
Security compliance is non-negotiable. No matter what.
Irrespective of whether you are into digital banking, card issuance, or lending, you must remember that your customer data, credentials, and documents are vulnerable to security hazards. Without strong risk management measures, you may risk exposing yourself and your customers to data breaches, cyber-attacks, and exorbitant fines from regulatory authorities. This is where cryptography, the science of protecting sensitive data saves the day, by delivering the highest levels of data protection.
Cryptographic Keys
Cryptography uses digital keys to encrypt and decrypt data with required levels of complexity for secure access and compliant operations.
So, what is a cryptographic key?
A cryptographic key refers to a string of characters in an encryption algorithm that helps randomly create the desired data. This key helps convert a plain text to ciphertext and vice-versa whenever data encryption and decryption happens. Efforts must ensure that only the authorized user has access to the key. The encrypted data must be stored securely for decryption without any discrepancy.
Lifecycle of a Cryptographic Key
The following process comprises the cryptographic key lifecycle.
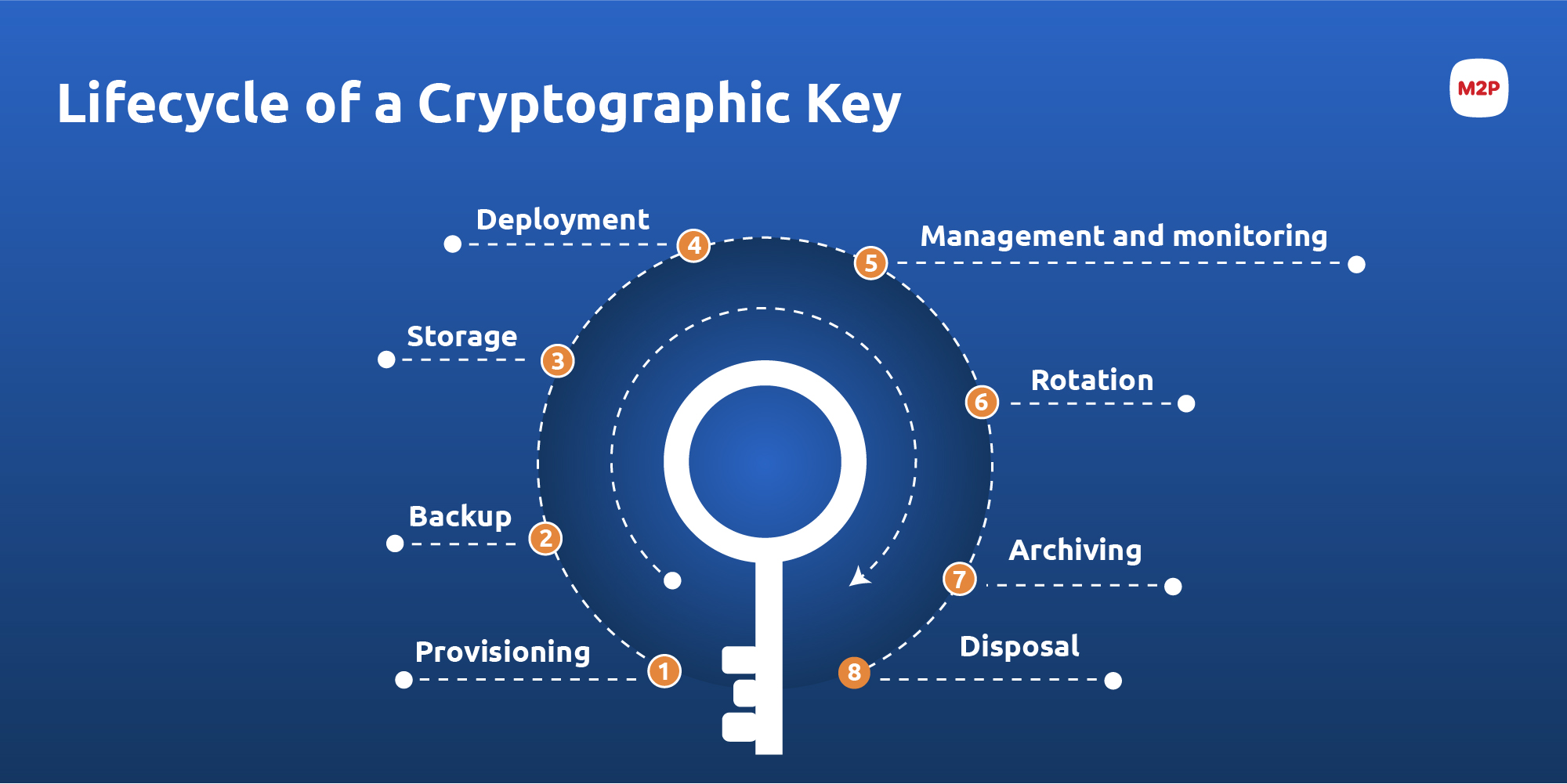
Provisioning –The provisioning process generates keys using a key management system, an hardware security module (HSM), or a Trusted Third Party (TTP) through random number generators. The keys should be strong enough to provide the necessary protection to secure the data.
Backup and storage- This is a critical step where a secure backup copy of the key is made. It should be available for future retrieval if the key undergoes any failures. Such backup keys are often stored in external media or other backup solutions. All private keys must be encrypted before being stored.
Deployment- The new key is installed electronically or manually into a secure cryptographic devices such as Hardware Security Module.
Management, Monitoring, and Rotation- Here, the keys are often controlled and monitored with respect to the industry standards and policies. The encryption key management system handles key rotation and deploys new keys as and when existing keys expire.
Archiving- The keys that are no longer in operation are stored here for an extended period. They might be required again in the future for associated data retrieval. The key, when archived, is encrypted for additional security.
Disposal- The keys are permanently destroyed here, when they are no longer needed. Before destruction, the key is analyzed and sometimes recovery is processes if necessary. A key can be removed from its operation using key destruction, key deletion, or key termination.
Generating, securing, and managing cryptographic keys can be multifaceted and complex, requiring support from information security and development teams.
So, how can you create, monitor, store, and optimally use cryptographic keys?
Simple. Install HSM.
So, what is Hardware Security Module (HSM)?
Hardware Security Module (HSM) is a device that provides a wired security solution for the wireless world. It is a dedicated cryptographic processor that offers a secure, tamper-resistant environment specifically designed to protect identities, devices, and cryptographic key data throughout its lifecycle.
HSM protects any data in use, transit, and rest, for encryption, decryption, authentication, and key management. In toto, it serves as a ‘trust anchor’ to ensure compliance, simplify audits, generate, and store keys.
Types of HSMs
HSMs can be broadly classified (as listed below) based on the levels of functionality and compliance with different security standards.
· General Purpose (GP) HSM
· Transaction HSM
General Purpose (GP) HSM
Wherever there is sensitive data, and the need for encryption prevails, GP HSM is indispensable. It generates powerful cryptographic commands that can safely encrypt and decrypt information for any application.
Sample use cases for general purpose HSM are:
· Symmetric key management for database encryption
· Asymmetric keys management for digital signature creation
· Certificates to support Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
· Crypto wallets
GP HSM supports compliance with the following standards.
· PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard)
· PCI 3DS (Payment Card Industry 3-Domain Secure)
· GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)
· FISMA (Federal Information Security Management Act)
· FedRAMP (Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program)
· ICAM (Identity, Credential, and Access Management)
· eIDAS (Electronic Identification and Trust Services)
Transaction HSM
Also known as payments HSM, this security module has advanced security features compared to the general-purpose counterpart. Transaction HSM enforces dual control using payment-specific cryptographic commands to ensure sensitive information never leaves the HSM. The PCI SSC compliance mandates the use of payments HSM for the use cases below.
· When payment transaction processing happens, this supports card, user and cryptogram validation
· Helps in processing EMV transactions
· Generates key and injects it
· Helps facilitate highest security when keys are shared with third parties
· Used for generating, managing, and validating PIN
· Enables electronic funds interchange, Electronic funds transfer at point of sale (EFTPOS), and ATM transactions
· For payment cards and mobile applications, it helps in generation of payment credentials
· Enables point-to-point encryption (P2PE), key management and secure data decryption
· With payment HSM, cash-card reloading is made hassle-free
· Facilitates PIN block translation when network switch of POS and ATM transaction takes place
Transaction HSM supports compliance with the following standards:
· PIN (Personal Identification Number) Security
· P2PE (Point-to-Point Encryption)
· 3DS (ACS- Access Control Server & DS- Directory Server)
· Card Production
· TSP (Token Service Provider)
· SPoC (Software-Based PIN Entry on COTS)
· CPoC (Contactless Payments on COTS)
Are HSMs trustworthy?
Absolutely!
HSMs have high accuracy and are implanted in a secure and sealed environment. This acts as the trust factor for every organization to implement. As HSMs work on a dedicated firewall, they never get exposed to the public internet and thus ensure maximum security. The hardware is designed to give a high input with minimal resource usage. This is how cryptographic keys and data are protected optimally.
High on protection
HSMs are commonly used to protect identities, transactions, and applications. They protect the cryptographic keys by creating a trustable environment in which processes such as encryption, decryption, and authentication are equipped and secured. They follow industry regulations and standards such as PCI DSS, FIPS 140–2, European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation, Domain Name System Security Extensions, and Common Criteria.
How HSM enables maximum security?
HSMs offer the ultimate protection for all the critical functions involved in payment applications and databases. Hardware Security Modules come with many features that cannot be overlooked, as they help organizations maintain a secure transaction infrastructure.
· HSMs are equipped with a secure design that meets all the security standards and adheres to the Federal Information Processing Standardization (FIPS) 140–2.
· The operating system in HSM is always security-focused.
· The higher levels of trust and authentication ensure the maximum security of the sensitive data and cryptographic keys.
· Automated lifecycle tasks and protective mechanisms are quick and efficient.
· The key is maintained only in the HSM, exempting the possibility of malicious attacks that might occur virtually.
· HSMs enable application integration with the help of APIs.
Versatility of HSMs
Businesses should use HSMs to safeguard the sensitive information pried by countless threats they might encounter. In day-to-day applications, HSMs secure data generated across banks, websites, cryptocurrencies, smart meters, mobile payments, medical devices, PINs, identity cards, and digital documents.
And the buck doesn’t stop here. HSM protects digital signing, ensures compliance, and helps in key generation and management. Wherever financial transactions happen, HSMs provide that additional layer of security.
Today physical HSMs are transitioning to the cloud. Cloud HSM or HSM as a Service (HSMaaS) hosts encryption keys and cryptographic operations with FIPS 140–2 Level 3 certified modules.
Want to know more about HSMs?
Contact us at business@m2pfintech.com
Subscribe to our newsletter and get the latest fintech news, views, and insights, directly to your inbox.
Follow us on LinkedIn and Twitter for insightful fintech tales curated for curious minds like you.




0 Comments